A definitive guide for HIPAA compliance among remote workers
HIPAA compliance lies at the heart of the U.S. healthcare system. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is the foundation upon which patient information is protected and there is no excuse for anyone associated with healthcare not to abide by HIPAA to the letter of the law.

And that includes working remotely.
When HIPAA was enacted on August 21, 1996, the concept that millions of healthcare workers would be accessing patient data from home or outside the walls of their hospitals or health practices was fantasy. The internet was in its formative years, the first iPhone was more than a decade away and there was a clear distinction between home and ‘the office’. Then came the digital revolution, followed by the COVID-19 pandemic, and before you could say ‘patient confidentiality’, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services was raising concerns about the risk of using remote access systems that lack HIPAA compliance features1.
With 36.2 million Americans predicted to work remotely by 2025 – an 87% increase on pre-pandemic levels2 - it has never been more important for health executives and staff to understand the risks of working with protected health information and the need to ensure the maintenance of HIPAA compliance regardless of where that work is done. To assist with that cause, this definitive guide will provide them with the information they need to navigate HIPAA compliance in the modern world and ensure patient confidentiality remains their highest priority.
What is HIPAA compliance?
HIPAA is an acronym for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, a federal law that was enacted to protect patients’ protected health information (PHI). The Act is designed to ensure only patients and the organizations working with and handling their PHI can access such information, with the likes of healthcare providers, insurers and business partners needing to comply with the law. Failure to do so can result in financial penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, while criminal penalties can be imposed for intentional breaches including potential imprisonment3.
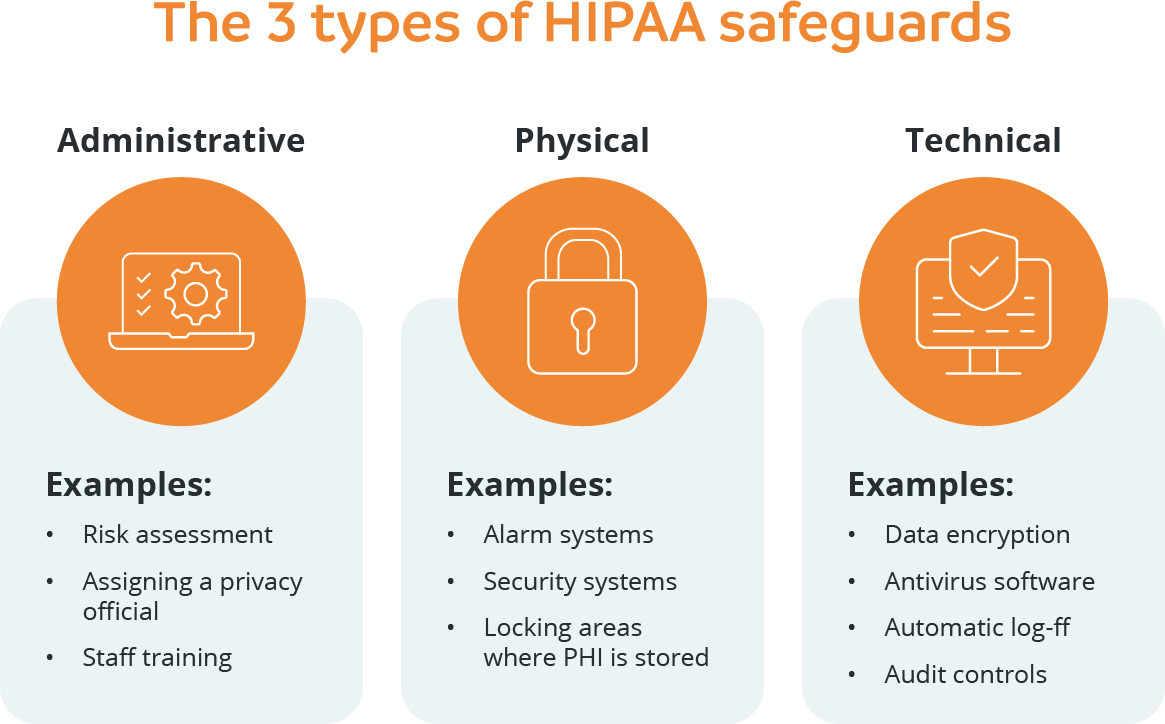
Source: The Ultimate HIPAA Compliance Checklist for 2023 (secureframe.com)
Why is HIPAA compliance important?
Patient confidentiality is a major concern for the healthcare sector, with a record 40 million people affected by cybersecurity breaches in the first half of 20234. HIPAA compliance puts a legal responsibility on hospitals and health services to do what is needed to avoid adding to statistics such as:
- About 95% of the U.S. population had their medical information disclosed between 2009 and 20215
- 95% of all identity theft incidents stem from stolen healthcare records, with such information worth 25 times as much as credit card details6
- 34% of healthcare data breaches come from unauthorized access or disclosure of PHI7
- As of September 30, 2023, the Office of Civil Rights had settled 137 cases of HIPAA violations for almost $137 million8
Risks of remote work on HIPAA compliance
Let’s make one thing clear – remote workers are not the issue when it comes to maintaining HIPAA standards. Rather, it is about the systems and support they have access to outside the traditional hospital or health setting. One 2021 study found that only 20% of IT teams had provided adequate tools and resources to support staff working remotely long-term and while that has likely risen in the wake of COVID-19, several remote work risks remain.
- Unsecure internet access: connecting to a secure network is essential when accessing patient files but what happens when a remote worker is unable to enjoy the seamless connection of their office-based colleagues? The risk arises of them seeking shortcuts via channels or networks that lack the necessary security measures, hence why it is essential for healthcare IT departments to ensure premium network and internet access to their remote workers. This extends to remote workers who fail to properly dispose of physical files.
- Paper-based PHI: despite the digital boom, many healthcare practices continue to cling to paper-based procedures for parts of their operations. From medical coding and billing to revenue cycle management, remote workers may be handling printed files that contain sensitive patient data and even the most harmless public exposure (eg: family members, housemates) can result in compliance officers issuing a HIPAA violation.
- Inadequate training: with health entities and business associates required to renew HIPAA certifications annually, compliance training programs are a key component of annual planning. A lack of proper training makes organizations vulnerable to HIPAA violations and nowhere is that risk greater than with remote workers. Out of sight should not mean out of mind and it is essential to devise engaging compliance training that is easily transferable to people working from home or remotely.
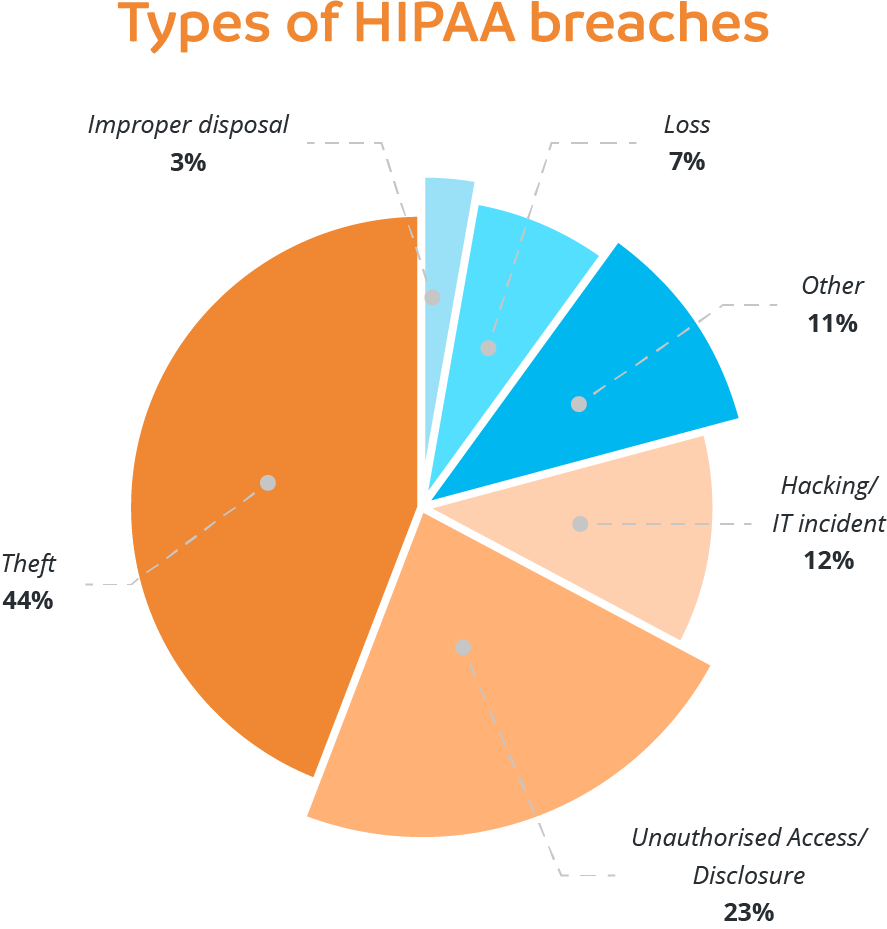
Source: Discover the top 3 causes of HIPAA violations and their simple solutions (calyptix.com)
4 tips for a HIPAA-compliant remote workforce
- Password security: healthcare providers need to ensure remote workers are not only logging in securely to their shared networks but that their home wireless router traffic is password protected. Advise them against using default passwords as they are typically provided for all to see on the side of the router and ensure unique and different passwords for any personal devices that have access to patient information. As for a tip on creating a secure password, it has been estimated it would take a hacker 438 trillion years to crack a password that is 18 characters long that contains upper and lowercase letters, symbols and numbers9
- Encryption tools: sharing sensitive information with colleagues is par for the course in the health sector and it should equally be the norm for that process to never unfold without using encryption tools. While every effort should be made to avoid sending PHI via email, solutions such as Sharefile adds a crucial layer of protection. It is also highly recommended to invest in a virtual private network (VPN), which establishes a protected network connection when using public networks. Remote work may see staff spread across different locations but they will effectively be connected to a private network regardless of where they are logging on.
- Workspace security: while some sectors may be able take a relaxed approach to their remote staff’s workspaces, health practices do not have that luxury. Leaving computers open and patient details unattended at home (or worse a coffee shop) can result in embarrassing and costly HIPAA violations. Installing a lock on a home office is advisable, while privacy screens for monitors can stop passersby from unintentionally seeing sensitive details. Physical documents are another concern. It may seem harmless to leave printed PHI on desks or printers in home offices but it is simply not worth the risk of a security breach. The best advice? Act at home as one would in the hospital or health practice.
- Compliance training: HIPAA education is a vital component of any healthcare practice but it is far too easy for remote workers to slip under the radar. While organizations may already have compliance programs, there is an urgent need for many of them to amend or rewrite such efforts to address the rise of remote work. It has been estimated that almost 50% of cybersecurity-related breaches happen due to employee carelessness10, highlighting why anyone who works with PHI should complete training that outlines HIPAA violations and how to avoid them regardless of their geographic location with a health service.
Questions to ask a prospective outsourcing provider
The success of remote work has also resulted in an increasing number of healthcare providers investing in outsourcing to support their operations. From revenue cycle management, contact center and patient access to medical coding and high-volume back-office tasks, quality offshore providers are highly skilled at sourcing the right people and supporting clients with HIPAA compliance and patient data safeguards. Issues to consider when engaging an outsourcing provider include:
- What is their password policy?
- Who will test the system security?
- Is there a policy for destroying media (eg: paper documents) at the end of the contract?
- Do staff receive training in PHI security?
- Are there pre-employment screenings?
- Do staff work in an open-plan office or secure room?
- Does the provider have controls to prevent ransomware attacks?
- Can staff take laptops home or use their own devices?
- Are staff allowed to download and install tools on their computer?
Summary
The healthcare sector’s adherence to HIPAA compliance is one of the great comforts for patients. Crucially, that commitment remains regardless of whether a team member is handling PHI in a hospital, health practice or remote work setting. The COVID-19 pandemic inspired a generational change for working environments and it is reassuring to know that steps continue to be made to ensure a rise in remote workers coincides with a rise in public confidence in patient data security.
Patient care may be top priority but health administrators are facing a battle to balance the books in an industry where margins are low and ‘customer’ expectations are high. Discover why an increasing number of health executives are looking offshore to meet the needs of their hospitals and practices.
Reference:
[1] Baground (hhs.gov)
[2] Upwork Study Finds 22% of American Workforce Will Be Remote by 2025 | Upwork
[3] What are the Penalties for HIPAA Violations? 2023 Update (hipaajournal.com)
[4] Fewer, but larger, healthcare data breaches reported in the first half of 2023 (fiercehealthcare.com)
[5] 51 HIPAA Statistics Every Healthcare Entity Needs to Know in 2023 | UpGuard
[6] Largest Healthcare Data Breaches Reported in February 2022 (globenewswire.com)
[7] 25+ Alarming Largest Healthcare Data Breaches Statistics 2023 (techjury.net)
[8] Enforcement Highlights - Current | HHS.gov
[9] Are Your Passwords in the Green? (hivesystems.io)
[10] The Human Factor in IT Security: How Employees are Making Businesses Vulnerable from Within | Kaspersky official blog
Popular posts
Newsletter sign up
Business growth and efficiency improvement hints and tips delivered direct to your inbox.
Related Posts
5 benefits of outsourcing in the healthcare industry
When Fitch Ratings turned its eye to what was on the horizon for the healthcare industry in 2024, it did not mince its words. The credit-rating..
What is BPO in the medical industry?
Late last year, as many of us were reflecting on the year that was, global consultancy Deloitte instead gazed into its crystal ball to predict what..
How outsourcing is helping boost telehealth services
Given the choice, there’s no doubt most of us would prefer to live in a world where we had never heard of COVID-19. A world in which more than 7..
